Home > Parts Procurement > Batteries
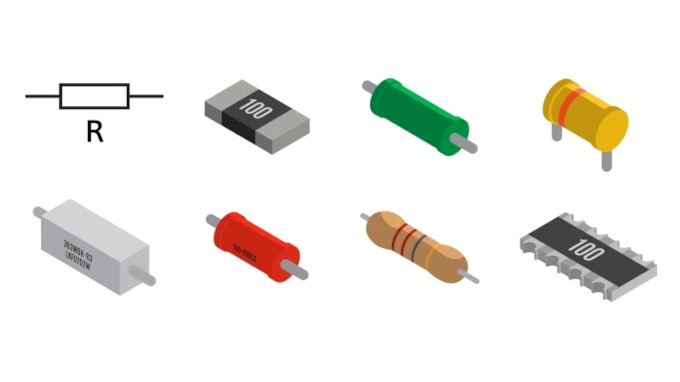
Resistors are essential components in electronic circuits, made from materials like thin films, cement, or resistance wires. They can also be integrated into ICs, hybrid circuits, or PCBs. Their resistance spans over 9 orders of magnitude, with tolerances and temperature coefficients critical for precision applications. Resistors have a maximum power rating that must exceed their expected energy dissipation, especially in power electronics. Stray inductance and capacitance are crucial in high-frequency applications, while noise is important for low-noise amplifiers. Resistors perform vital roles such as voltage dividing, current limiting, and biasing, making them indispensable in electronic equipment.







Silicon RF Capacitors Thin Film are miniaturized electronic components that employ silicon technology to offer high-frequency performance in radio frequency (RF) applications.
































XPC, FR-1, FR-2 are flame-retardant phenolic materials that are also highly punchable, they have excellent electrical, heat-resistant, moisture-resistant, flame-resistant and other properties as well as low cost. FR-3 is epoxy Copper Clad Laminate, it is flame retardant with high electrical properties.
CEM-1, which is a composite of paper and glass impregnated with epoxy resin, is the most popular substrate for SSBs. While not as low cost as XPC-FR or FR-2, CEM-1 has gained popularity because of its mechanical strength and also because of the relative unavailability of paper phenolic laminates.
CEM-3 is similar to FR4, but uses a composite material of a non-woven glass core and a woven glass surface instead of a full sheet of woven glass. It’s a flame retardant epoxy resin, copper-clad glass material, commonly used in double-sided PCBs.
“FR” is the abbreviation of flame retardant. As the board runs on electricity, it should be heat resistant. FR4 has much better heat resistance than FR1 and XPC due to the different composition of the layers.